
|
Biological Small Angle Scattering |

|
|

|
| ATSAS online | Forum | User information | EMBL Hamburg |
|
|
CRYSON manualWritten by D.Svergun, M.Malfois, M. Petoukhov and A. Shkumatov. © ATSAS Team, 1998-2009 Table of ContentsManualCRYSON is a reimplementation of CRYSOL, adopted to work with Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS) data. The following shortly describes the main differences between CRYSON and CRYSOL. For detailed description, see CRYSOL manual. If you use results from CRYSON in your own publication, please cite: IntroductionCRYSON is a program for evaluating the solution scattering from macromolecules with known atomic structure and fitting it to experimental scattering curves from Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS). As an input one can use a PDB file with an X-ray or NMR structure of a protein or a protein-DNA(RNA) complex. The program uses multipole expansion of the scattering amplitudes to calculate the spherically averaged scattering pattern and takes into account the hydration shell, D2O fraction as well as perdeuteration fraction for individual molecule. Given SANS experimental data, CRYSON can fit the theoretical scattering curve by minimizing the discrepancy (chi-square value). CRYSON smears the theoretical curves using the resolution function to take the instrumental distortion into account. Running crysonUsage: $> cryson [PDBFILE] [EXPDATA] [ILLRES] [OPTIONS] CRYSON accepts absolute as well as relative path to PDBFILE, EXPDATA or ILLRES. If no input files are given, the configuration is done in interactive mode. Generally, CRYSON uses same command line arguments and interactive configuration as CRYSOL. Here the main differences are outlined: Command-Line Arguments and Options Unique to cryson
Interactive Configuration Different from crysolIf no input files are given, interactive mode with same questions as in CRYSOL is started. Differences include:
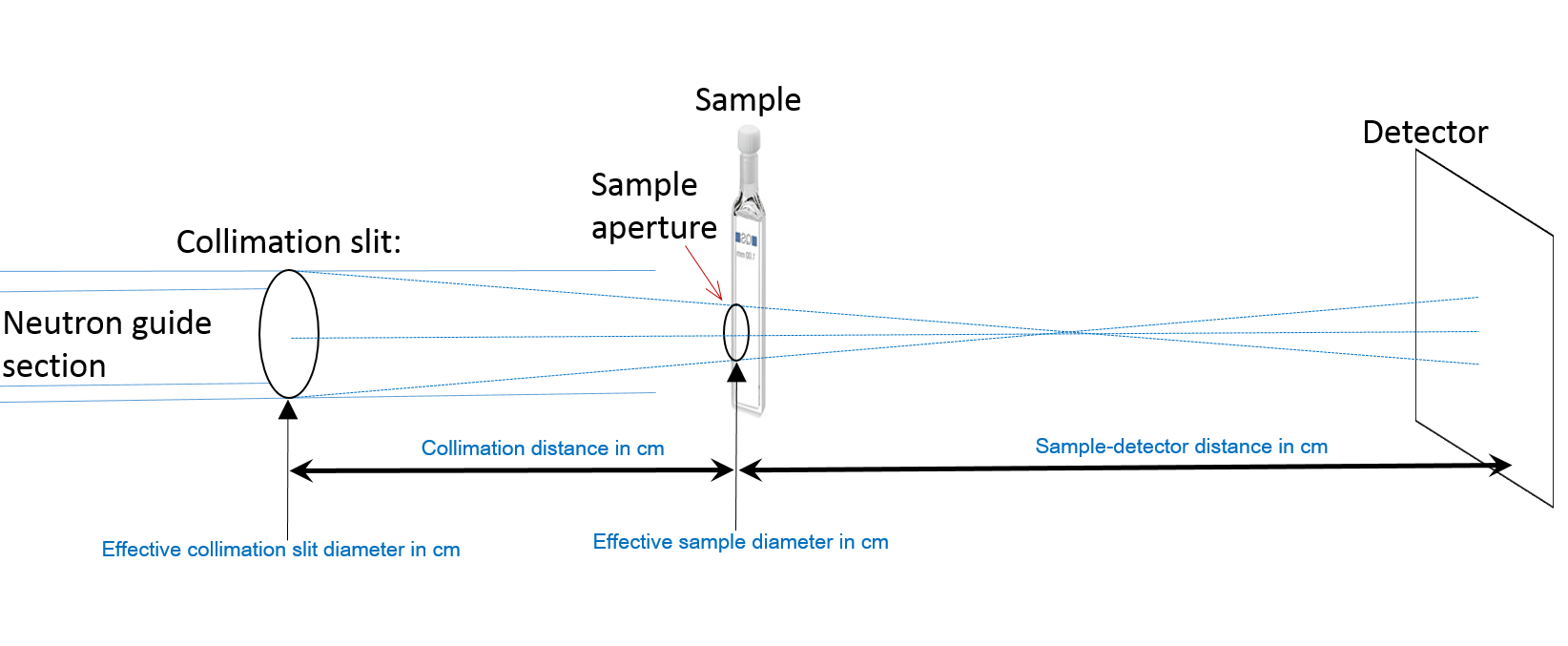
Runtime OutputSee CRYSOL manual Input Files Unique to crysonCRYSON uses both PDB file and SANS experimental data as input. An additional file (ill.res) required for smearing the theoretical curve has the following format (the numbers describe a setting at RISOE SANS instrument):
cryson Output FilesSee CRYSOL manual. ExamplesAll examples use tr.pdb, trd2o.dat and ill.res. They are included in the documentation directory of the installation package. Calculating scattering intensity without fitting$ cryson tr.pdb /lm 20 /D2O 0.5 Use CRYSON to calculate the scattering intensity from the PDB file. Maximum order of harmonics = 20 and D2O fraction = 0.5 Processing PDB files with fitting$ cryson "tr*.pdb" trd2o.dat /res ill.res Use CRYSON to calculate the scattering intensity from all PDB files, starting with 'tr' and ending with '.pdb'. Calculated theoretical curve is smeared using parameters in resolution file ill.res and fitted to experimental data trd2o.dat |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Last modified: March 19, 2015
© BioSAXS group 2015